1.4.1 Understanding Logical Domain Components
1.4.1 Understanding Logical Domain Components
A logical domain consists of virtual CPUs, virtual memory, and virtual I/Os.
- Virtual CPU
A CPU can be assigned to a logical domain in units of virtual CPUs (threads). In the SPARC M12/M10 system, one physical CPU (i.e., one socket) has multiple cores, each of which has threads. This means that a physical CPU has as many virtual CPUs as the number of threads. You can assign these virtual CPUs to a logical domain. Normally, assign the virtual CPUs to a logical domain in units of cores, considering the logical domain performance. - Virtual memory
Memory can be assigned to a logical domain in units of 256 MB. - Virtual I/O
I/O can be assigned to a logical domain in units of virtual I/Os. For example, a virtual disk is one virtual I/O, which can be used as a:- Physical disk- Physical disk slice- File from a file system such as ZFS or UFS- Logical volume from the ZFS or another volume manager
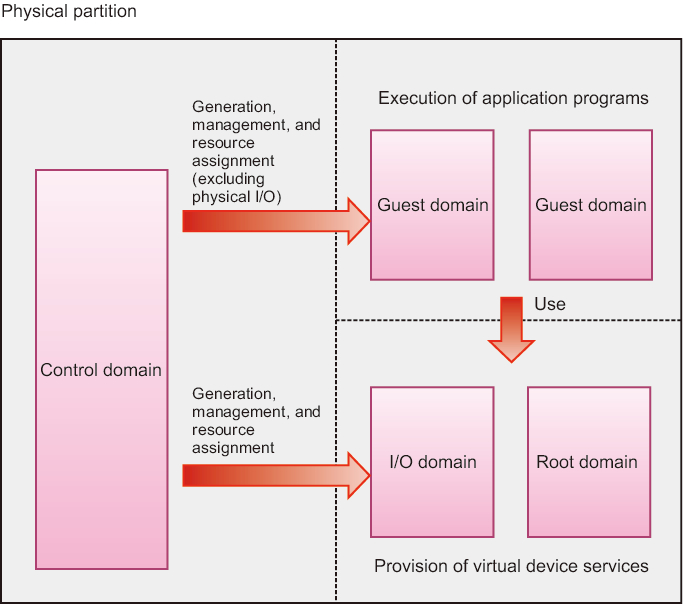
Logical domains are categorized by role as follows.
- Control domain
A control domain is a logical domain that creates and manages other logical domains and assigns resources to the logical domains. Each physical partition has only one control domain. Oracle VM Server for SPARC is installed on the control domain, where the management software Logical Domains Manager is running. - I/O domain
An I/O domain is a logical domain that provides virtual device services. The virtual device services include a disk, network, and console. - Root domain
A root domain is an I/O domain to which a PCIe root complex is assigned. A PCIe root complex is an entire PCIe bus, consisting of the PCIe bus, all PCI switches, and devices. Physical I/O devices belong to the root domain, which accesses them directly. - Guest domain
A guest domain is a logical domain controlled by the control domain. It uses virtual device services from an I/O domain. Normally, middleware and application programs run on the guest domain. Oracle Solaris runs independently on the guest domain, which can thus start and stop without affecting other guest domains. Virtual CPUs, virtual memory, and virtual I/Os can be dynamically added to and deleted from the guest domain. - Service domain
Service domain is a generic term for a domain that provides services to a guest domain. Specifically, it includes I/O and root domains.
|
Figure 1-18 Concept of the Relationship Between Logical Domains
|
|
< Previous Page | Next Page >