2.3 Relationship Between the CPU Configuration and the Number of Root Complexes
2.3 Relationship Between the CPU Configuration and the Number of Root Complexes
The 2-CPU configuration of the SPARC M10-4 consists of four root complexes, and the 4-CPU configuration consists of four or eight root complexes. A root complex consists of an I/O controller mounted on a processor and the PCI switches, PCI devices, etc. under the I/O controller.
The number of root complexes when a CPU memory unit is installed on site is kept at the default value of 4, by default. In this case, the system configuration can be kept as is since the I/O bus is not reconfigured, but the PCI card mounting rules are also kept, so they are the same as those for the 2-CPU configuration.
To change the number of root complexes to eight, the system administrator needs to change the XSCF settings to reconfigure the I/O bus reconfiguration. For details on the setting method, see the man page for the setpparmode(8) command or the Fujitsu SPARC M12 and Fujitsu M10/SPARC M10 XSCF Reference Manual. Changing the number of root complexes to eight increases the maximum number of mounted PCI cards. However, because device path names change with the reconfiguration of the I/O bus, system reconfiguration such as to set a device path name again may be required for any device path names used by applications.
| Order for M10-4 Only | Order for CPU Memory Unit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ordered Together With M10-4 (Installed at Factory) |
Ordered Separately From M10-4 (Installed on Site) | |||
| Without I/O Bus Reconfiguration | With I/O Bus Reconfiguration | |||
| Number of CPUs | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Number of root complexes | 4 | 8 | 4 | 8 |
Figure 2-1 is a hardware configuration diagram of the SPARC M10-4 with two CPUs. Figure 2-2 is a hardware configuration diagram of the SPARC M10-4 with four CPUs (four root complexes). Figure 2-3 is a hardware configuration diagram of the SPARC M10-4 with four CPUs (eight root complexes).
|
Figure 2-1 Hardware Configuration Diagram of the SPARC M10-4 With 2 CPUs
|
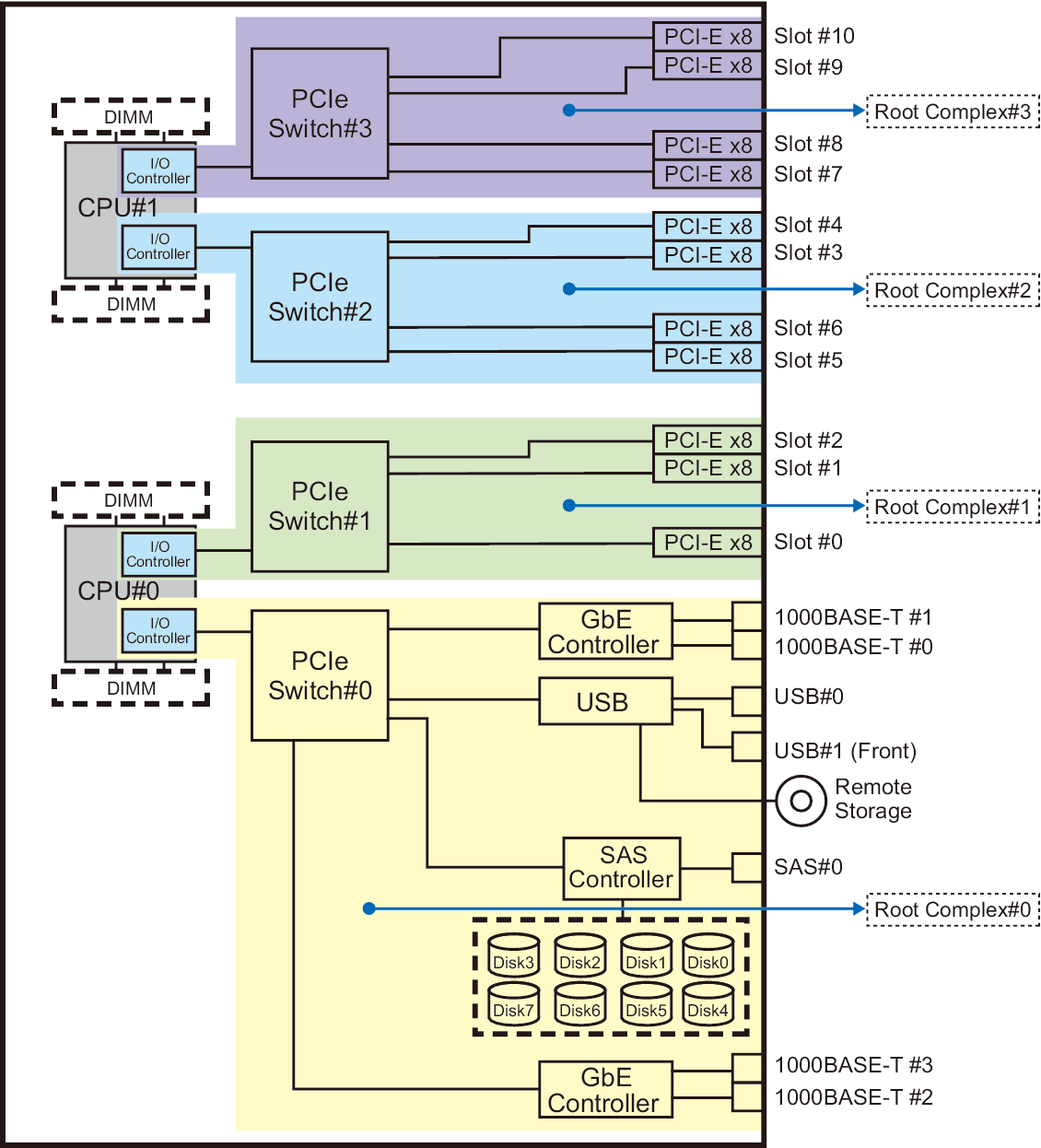
|
|
Figure 2-2 Hardware Configuration Diagram of the SPARC M10-4 With 4 CPUs (4 Root Complexes)
|
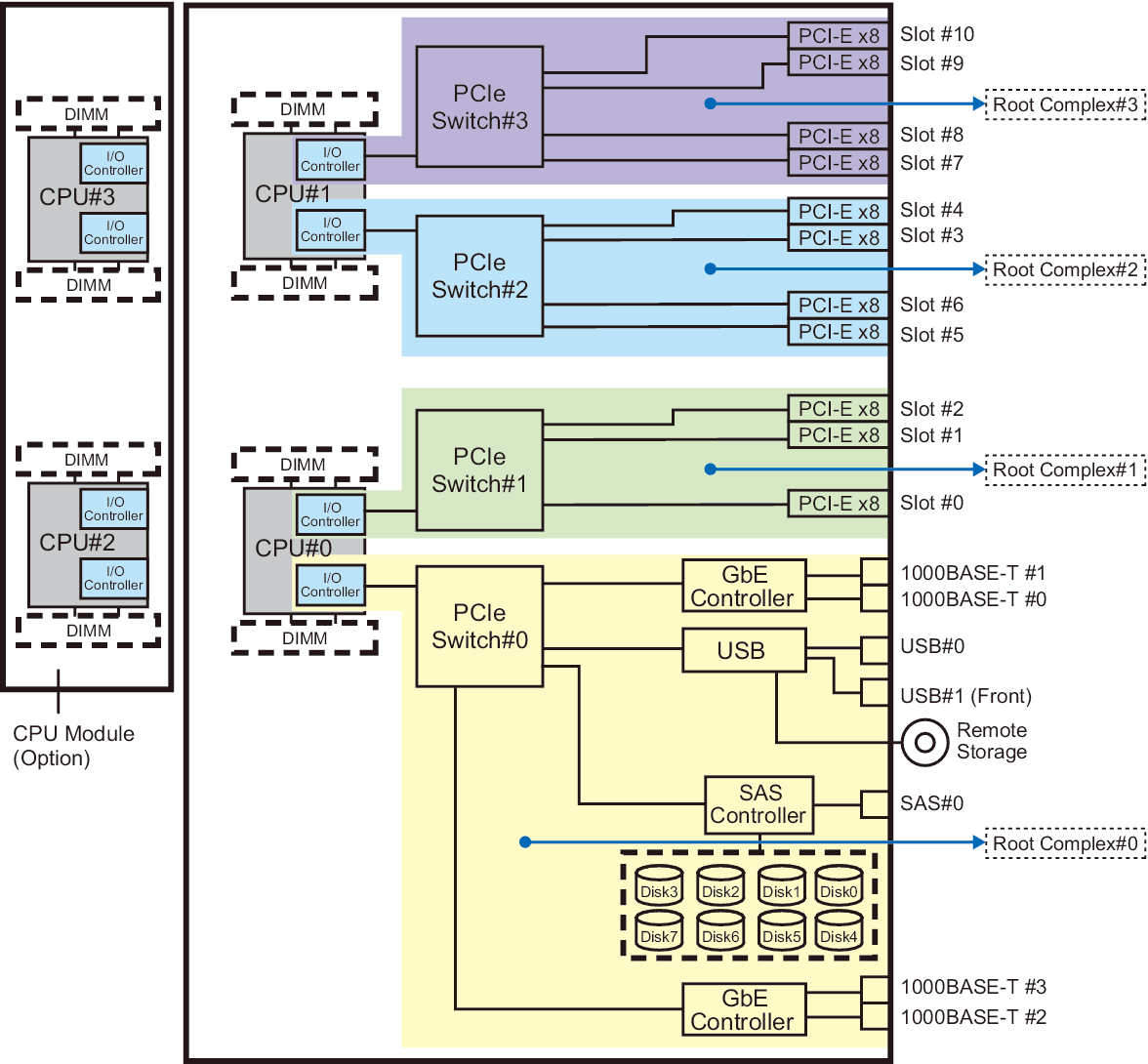
|
|
Figure 2-3 Hardware Configuration Diagram of the SPARC M10-4 With 4 CPUs (8 Root Complexes)
|
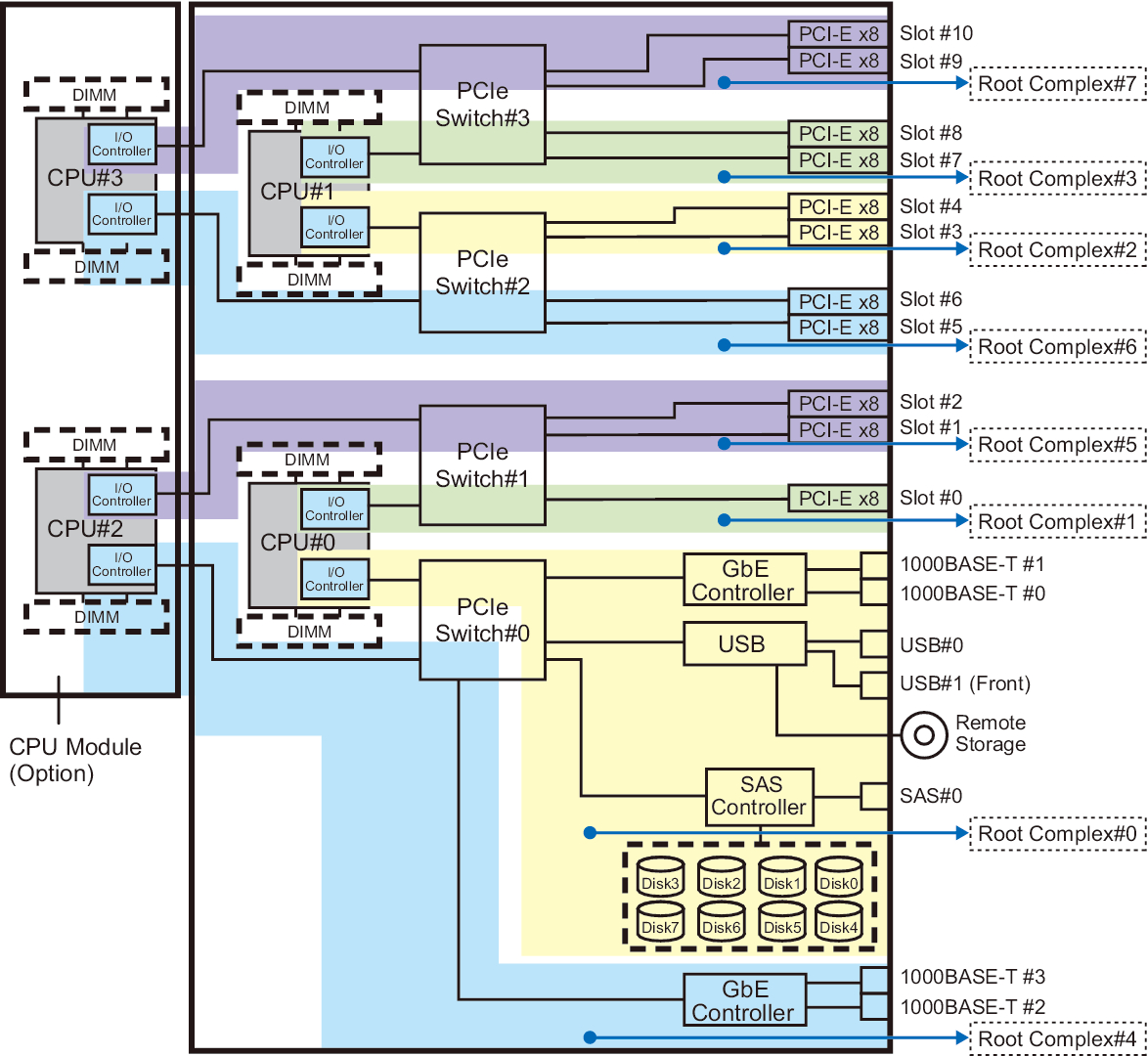
|
< Previous Page | Next Page >
