11.2.2 Checking the Physical Partition Configuration
11.2.2 Checking the Physical Partition Configuration
The showpcl command displays the configuration information for each physical partition or each logical system board that makes up the physical partition. The system administrator refers to a PCL (physical partition configuration list) when incorporating a logical system board into a physical partition.
You can check the PCL of the specified physical partition by using the showpcl command.
You can check the PCL of the specified physical partition by using the showpcl command.
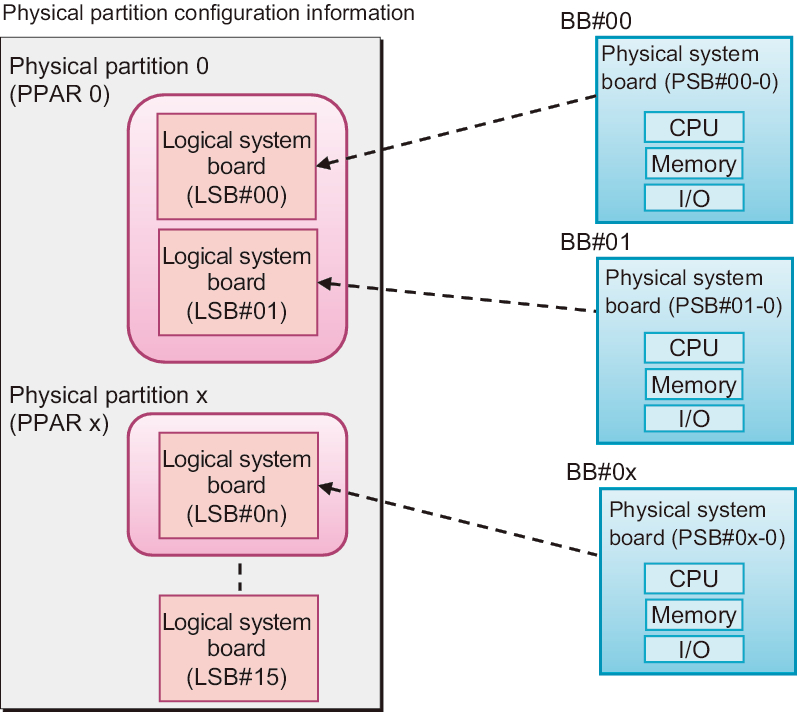
The mapping between the logical system boards (LSBs) on the physical partition and the physical system boards (PSBs) is determined by the PCL information. Figure 11-1 shows an example of a PCL mapping.
PSB refers to a hardware resource to configure a physical partition. Specify (or display) a PSB in xx-y format. xx is BB-ID, and y is fixed at 0.
PSB refers to a hardware resource to configure a physical partition. Specify (or display) a PSB in xx-y format. xx is BB-ID, and y is fixed at 0.
|
Figure 11-1 Image of the Mapping Between Logical System Boards and System Boards
|
|
Table 11-8 describes terms related to physical partitions.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical system board (PSB) | PSB stands for physical system board. The PSB consists of physical components (CPU, memory, and I/O) mounted in one SPARC M12/M10 chassis. In the SPARC M12-1/M10-1, a physical system board is a motherboard unit. In the SPARC M12-2/M12-2S/M10-4/M10-4S, a physical system board is a CPU memory unit (including lower (CMUL) and higher (CMUU)). A physical system board may be used as the unit representing a chassis, in maintenance for adding/removing/replacing a SPARC M12/M10 chassis. For a system in a building block configuration, a physical system board refers to one building block (BB). |
| Logical system board (LSB) | LSB stands for logical system board. Logical unit names are assigned to a PSB. Each physical partition has a set of logical system boards assigned to it. With one PSB number assigned to the logical system boards in the physical partition, they can be recognized in the system. LSB numbers are used to control the assignment of resources such as memory to the physical partition. |
| Physical partition configuration | This term refers to the partitioning of system hardware resources into independent units for software operation. A physical partition is a PSB cluster, and the system consists of one or multiple physical partitions. A physical partition is configured using the XSCF as follows. 1. Assign LSB numbers to the PSB. 2. Assign the PSB to a physical partition. 3. The physical partition operates with LSB resources and the LSB numbers. |
| Physical partition configuration information | This term refers to the hardware resource information configured for each physical partition or each LSB that makes up the physical partition. The setpcl and showpcl commands can set and display, respectively, the PCL. |
| Configuration policy | This policy can specify the unit of logical resources to be degraded for each physical partition when an error is detected in an initial hardware diagnosis. The configuration policy specifies a PSB or discrete resources as the degradation range. |
| I/O disabled (no-io) | This term refers to when the logical use of the I/O unit on the PSB is disabled in the physical partition. |
| Memory disabled (no-mem) | This term refers to when the logical use of the memory on the PSB is disabled in the physical partition. |
| PSB status | This status of each PSB shows the power status (power), diagnosis status (test), assignment status (assignment), incorporation status (connection), operation status (configuration), and degradation status (fault). You can learn the progress of PSB status change in the physical partition. You can refer to PSB status information by using the showpcl and showboards commands. |
| System board pool (SP) | This term refers to the state of BBs (PSBs) that do not belong to any physical partition. For a physical partition with a high CPU or memory load, a BB (PSB) can be added to this physical partition. At the point when the system board is no longer needed, it can be returned to the system board pool. |
A PCL is a definition list for setting the information for one LSB. You can set LSB information for up to 16 LSBs per physical partition.
Table 11-9 lists details of physical partition configuration information. The configuration policy can be set only in the SPARC M12-2/M10-1/M10-4 systems.
Table 11-9 lists details of physical partition configuration information. The configuration policy can be set only in the SPARC M12-2/M10-1/M10-4 systems.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| PPAR-ID | ID of a PPAR |
| LSB number | LSB number |
| PSB number | PSB number assigned to an LSB. The same PSB number cannot be assigned to another LSB within the same physical partition. |
| no-mem (Memory nullification option) |
True: Memory cannot be used False: Memory can be used (Default) |
| no-io (I/O nullification option) |
True: I/O not incorporated False: I/O incorporated (Default) |
| Configuration policy | FRU: Degradation is performed in units of field replaceable units (FRUs). (Default) PSB: Degradation is performed in units of PSBs. System: Physical partitions are powered off, in units of physical partitions, without degradation. |
| Physical partition status | This indicates the physical partition operation status, such as whether the power is off or whether POST initialization has completed. For detailed definitions, see the showpcl(8) command man page or the Fujitsu SPARC M12 and Fujitsu M10/SPARC M10 XSCF Reference Manual. |
Operation Procedure
- Execute the showpcl command to check PCL information.
The following example displays the set PCL information for PPAR-ID 00.
| XSCF> showpcl -p 0 PPAR-ID LSB PSB Status 00 Running 00 00-0 04 01-0 08 02-0 12 03-0 |
- The following example displays the set PCL information for PPAR-ID 00 in detail.
| XSCF> showpcl -v -p 0 PPAR-ID LSB PSB Status No-Mem No-IO Cfg-policy 00 Running System 00 - 01 - 02 - 03 - 04 01-0 False False 05 - 06 - 07 - 08 02-0 True False 09 - 10 - 11 - 12 03-0 False True 13 - 14 - 15 - |
| Note - For details of physical partition configurations, see the Fujitsu SPARC M12 and Fujitsu M10/SPARC M10 Domain Configuration Guide. |
< Previous Page | Next Page >